The long shadows of America’s growing debt
Financial Times
Unlock the Editor’s Digest for free
Roula Khalaf, Editor of the FT, selects her favourite stories in this weekly newsletter.
In March, Phillip Swagel, director of the US Congress’s independent fiscal watchdog, told the Financial Times that America risked a Liz Truss-style market shock with its soaring debt pile. His reference to the former British prime minister’s “mini” Budget in September 2022 — which led to a sudden surge in UK government bond yields and ructions across financial markets — was an attempt to fend off complacency, rather than a warning of imminent implosion.
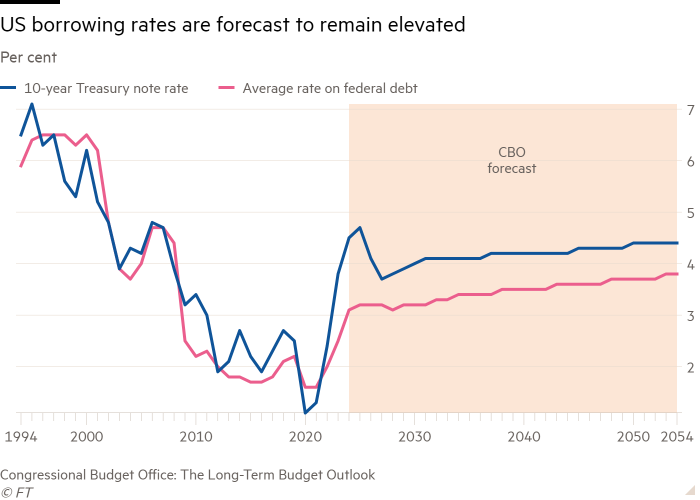
Swagel is right to sound the alarm. America’s debt is on an unsustainable path. The Congressional Budget Office projects America’s debt-to-GDP ratio will surpass its second world war high of 106 per cent by the end of the decade, and keep rising. The total deficit is forecast to average 5.5 per cent of GDP until 2030 — about 2 percentage points higher than the post-1940 mean. Net interest payments, which are currently around 3 per cent of GDP, are expected to keep creeping upward too.
Politics is an aggravating factor. Both the Democrats and Republicans heed the importance of fiscal responsibility in theory, but neither is prepared to tighten belts, particularly in an election year. Joe Biden proposed a $7.3tn budget plan for 2025. His presidential rival, Donald Trump, has vowed to renew tax cuts enacted during his time in the White House, which could add another $5tn to the nation’s debt, according to the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget, a think-tank.
America’s growing debt puts upward pressure on its longer-term borrowing costs. Lax fiscal policy can raise inflation expectations and the perceived risk of holding debt for long periods. The hefty pipeline of debt issuance will also need to be absorbed by more price-sensitive investors, with the Fed now engaging in quantitative tightening.
Elevated yields raise the cost of borrowing and could undermine economic growth. There is an increased vulnerability to rapid and disruptive movements in US bond markets. This has knock-on effects for credit and financial stability abroad too, since US Treasuries act as a benchmark for pricing debt globally. IMF research suggests that a 1 percentage point spike in US rates led to a 90 basis point rise in other advanced economies’ bond yields, and an increase in emerging markets of 1 percentage point. Restraints on domestic and global growth will only heighten the debt reduction challenge.
America’s
The full article is available here. This article was published at FT Markets.
Comments are closed for this article!